A separate cross-industry survey1 of 48 top level electronics industry managers, including CEOs and COOs, by Porsche Consulting reveals productivity, reliability, flexibility, sustainability and attractiveness to employees as five key objectives underlying companies’ efforts to optimize their production networks. The results indicate that while 96 percent of companies have embarked on smart factory transformation to achieve these objectives, only eight percent of surveyed organizations have fully realized their expectations. This is due to a limited view that focuses on the automation of physical processes.
Global Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) companies are facing various challenges, from supply chain disruption and a shortage of skilled labor to the need for more agile processes and pressure to demonstrate greater circularity in their operations. Digitalization and automation – including the use of robotic technologies – are not only crucial avenues for enhancing productivity, reliability, flexibility and sustainability, but they are also key drivers in the development of smart factories.
Juntian Dong, Partner, Head of Industrial Goods, Porsche Consulting China
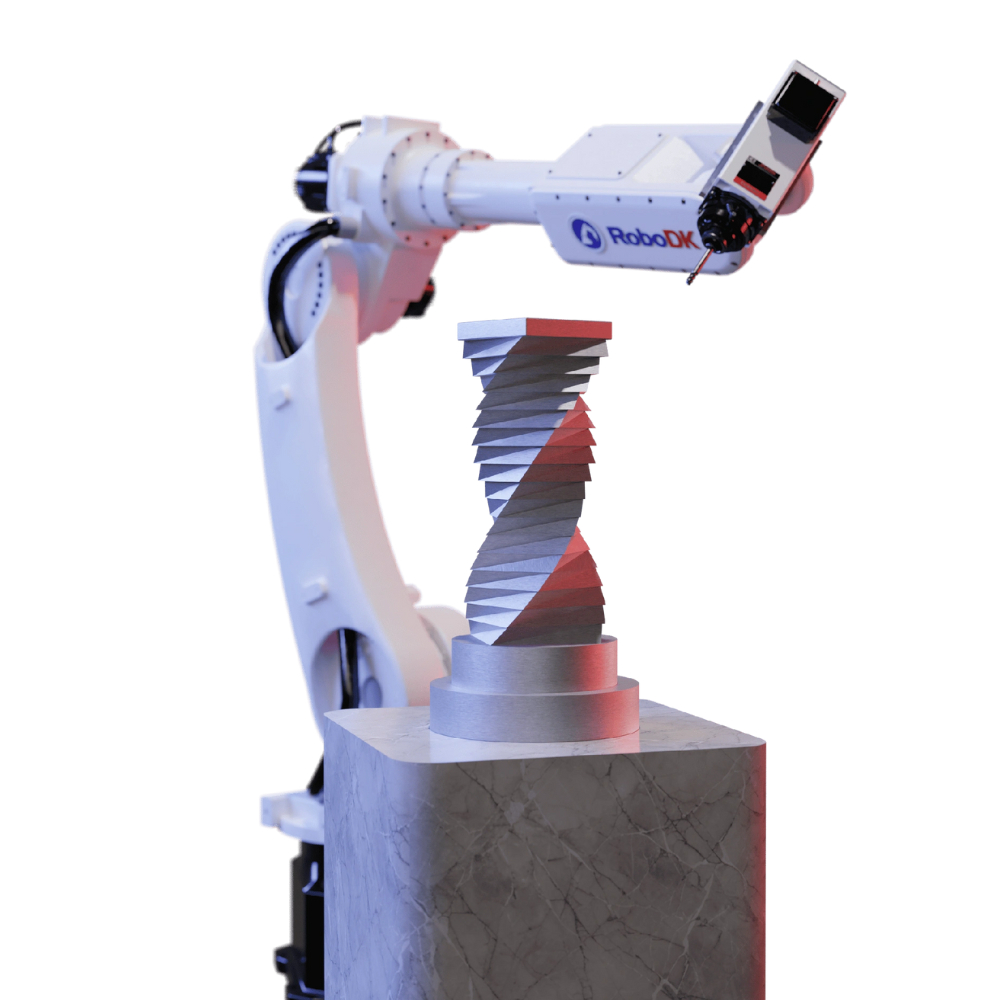
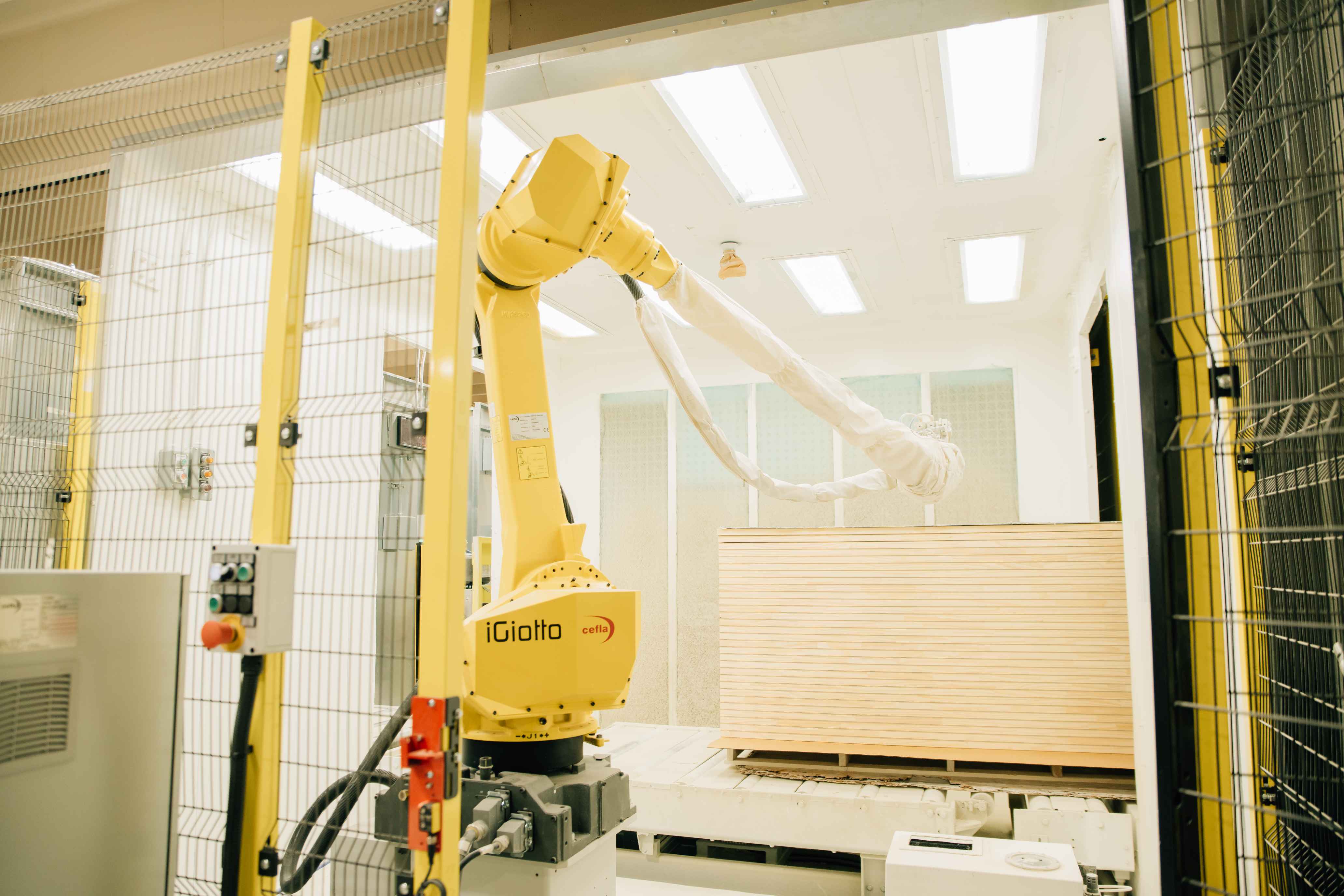
The paper highlights the use of robotic sanding and polishing in modern electronics manufacturing, where it is used to maximize the cosmetic appearance of consumer products such as smartphones. It explains how the efficiency of robotic finishing is often compromised by hard-to-use offline programming tools and problems. Deviations can also occur when virtual robot code is transferred to physical code, causing defects that require time-consuming manual fine-tuning to rectify, especially for 3D geometries. From an operational and commercial perspective, these challenges result in higher engineering costs for electronics manufacturers, together with greater reliance on expert resources, reduced product yields and increased waste.
The paper explains how these obstacles are addressed by ABB Machining PowerPac, part of ABB’s market-leading RobotStudio offline programming tool suite. Machining PowerPac allows automatic generation of CAD path code, achieving accurate representations of actual part surfaces and skipping the time-consuming traditional point-by-point commissioning process.
The white paper uses the findings of a study of historical project programs to demonstrate the improvements that Machining PowerPac can deliver. These include dramatic reductions in the time needed to generate a robot path – from four hours to three minutes – and improvements in robot cycle time of up to 33 percent, enabling more parts to be produced with the same equipment.
Other highlights include potential savings of 8,000 prototype parts due to reduced cosmetic damage from path design flaws, equivalent to 2.37 tons of aluminium alloy. These improvements in time, quality and productivity, together with additional savings in materials and energy, typically enabled investments in Machining PowerPac to be recouped within three months, with a projected ROI over 18 months of more than 1200%.