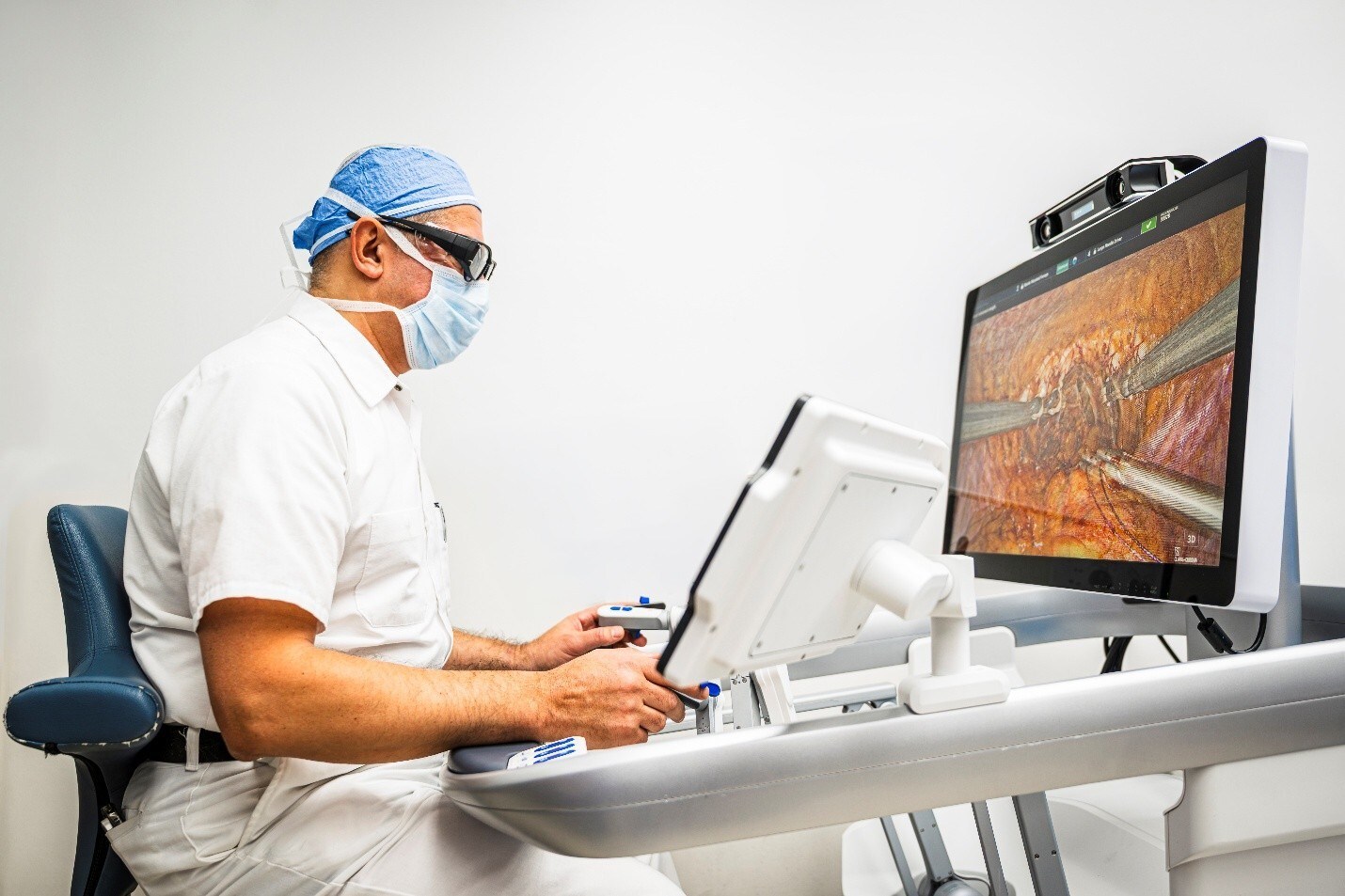
MMI Receives FDA IDE Approval for First Robotic Microsurgical Study Targeting Alzheimer’s Disease
The REMIND study will evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the Symani® Surgical System for restoring lymphatic drainage pathways in Alzheimer’s patients.
Image Courtesy: Public Domain
MMI (Medical Microinstruments, Inc.), a robotics company dedicated to increasing treatment options and improving clinical outcomes for patients with complex conditions, announced the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) approval of an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) for a clinical study using a novel microsurgical intervention for Alzheimer’s disease.
The feasibility study, entitled REMIND, Robotic-Enabled Microsurgical Intervention for Neurodegenerative Disease, will collect safety and effectiveness data of the Symani® Surgical System and microsurgical techniques to reestablish lymphatic drainage pathways in the deep cervical lymph nodes (dCLNs) of patients with Alzheimer’s and confirmed lymphatic obstruction. The primary endpoint of the study is device-related serious adverse events through 30 days post procedure. Additional endpoints include adverse events, biomarker and imaging changes, and cognitive assessments through six months post procedure.
Breakthrough scientific discoveries over the past decade have improved our understanding of lymphatic vessels in the central nervous system and are exposing the potential need for microsurgical interventions for patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. This potential therapeutic pathway, further enabled by robotics, could improve the clearance of harmful proteins like amyloid beta and tau and serve as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease.
“This FDA approval is more than a milestone for our company—it’s a signal of what’s possible in science when we bring together the right experts, technology, and research,” said Mark Toland, CEO of MMI. “We’re at the threshold of a new era in microsurgery; one where robotic precision could play a central role in unlocking novel treatment pathways for devastating diseases like Alzheimer’s. With REMIND, we’re just beginning to explore the extraordinary potential of robotic lymphatic intervention in redefining a critical standard of care.”
Operating on the dCLNs requires precision at a supermicrosurgical scale, as these lymphatic vessels can be 0.2mm in diameter, equivalent to the thickness of 2 sheets of paper. Very few surgeons are able to dissect and suture such small, delicate structures in a reproducible manner without robotic assistance. This first ever surgical approach involves establishing a precise connection of lymphatic vessels or lymphatic nodes in the neck to neighboring veins utilizing Symani’s robotic precision, which would allow for the draining of neurotoxins from the brain and could support reduced variability in outcomes.
“The REMIND study offers the potential to open an entirely new chapter in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease," added Kate Rumrill, Chief Scientific Officer of MMI. “Bringing robotic precision to more surgeons stands to change patient lives and medicine. Initiating such critical research may help pave the way for further studies to explore the promise of lymphatic microsurgery in improving the lives of more than 7 million Americans impacted by Alzheimer’s and bringing renewed hope to the caregivers who support them every day.”
The company is partnering with a select group of leading research institutions in the U.S. and Europe to initiate patient enrollment in this landmark study in the very near future. As MMI deepens its presence into critical clinical areas, this and future studies will generate essential data to strengthen the evidence for expanded robotic microsurgical applications.